Bloomberg Businessweek: Apple's Electric Car Fail II
Author, Businessweek. Source, Bloomberge Mailshot.
It was Steve Jobs who first floated the idea of a car at Apple. In the late 2000s, in a typically grand pronouncement, the company’s co-founder and CEO declared internally that Apple should have dominant technologies in all of the spaces in which people spend time: at home, at work and on the go. For many Americans, being in transit means being on the road, sometimes for hours a day. “We talked about what would be this generation’s new Volkswagen Beetle,” recalls Tony Fadell, who was the senior vice president of the iPod division under Jobs. In the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, with American car companies on the brink of failure, the Apple chief executive even floated the idea of acquiring General Motors Co. for pennies on the dollar.
That scheme was quickly abandoned, in part because Apple decided it would be a bad look and in part because of the need to focus on the iPhone. But in 2014, seeking a new multi-hundred-billion-dollar revenue stream, Cook began to focus again on cars. Apple executives weighing whether to enter the market joked with one another that they’d rather take on Detroit than a fellow tech giant: “Would you rather compete against Samsung or General Motors?” The profit margins in cars were far lower than in consumer electronics, but Apple was coming off a stretch during which it had reshaped not only the music industry but the mobile phone market. To its supporters, the idea of getting into automobiles had the potential to be, as one Apple executive puts it, “one more example of Apple entering a market very late and vanquishing it.” While the initial prototypes operated like traditional cars, these supporters eventually pursued more radical redesigns, invoking a transportation technology experience they said would “give people time back.” The ultimate plan was a living room on wheels where people who no longer needed to drive their cars could work or entertain themselves with Apple screens and services instead.
Read more: Apple’s 10 Biggest Challenges, From AI to China
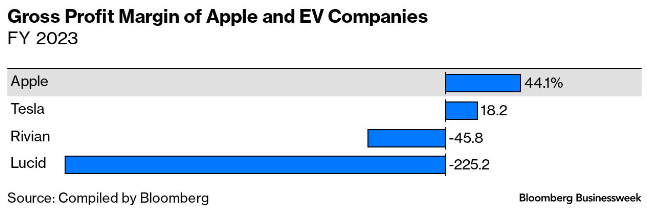
But before sketching out its own designs, Apple considered acquiring Tesla. At that point the electric-car maker’s success was far from assured, and its value was less than $30 billion, or a 20th of what it is today. Adrian Perica, Apple’s head of corporate development, held a series of meetings with Elon Musk. But Cook, who’d succeeded Jobs three years earlier, shut the deal down while negotiations were still at an early stage. Apple’s chief financial officer, Luca Maestri, formerly the General Motors CFO in Europe, argued that the car industry’s low margins were something the tech company couldn’t easily overcome.
Although the Tesla idea was abandoned, the ambitions didn’t go away. Apple’s newly minted hardware chief, Dan Riccio, received approval to start building a car engineering team, and he hired hundreds of engineers from the auto industry for what came to be known as Project Titan. The team working on the car was called the Special Projects Group. Within the company, it was difficult to find spare engineering talent, with attention focused on preparing for the upcoming Apple Watch release and, later, the iPhone X, but Riccio managed nonetheless to poach several dozen engineers from other projects. Early on, Jay Leno gave the team a tour of his garage for inspiration and a minor lesson in automotive history. Around this time, Riccio, rallying his troops, often would close with “Boys, let’s go build a car!”
The infighting began almost immediately. Maestri, the CFO, remained a skeptic, as did Craig Federighi, Apple’s software engineering chief, who had to donate personnel to what he considered a vanity project. Jony Ive, Apple’s design chief at the time, was more ambivalent, pushing for full driving autonomy but also expressing doubts about the wisdom of the endeavor. Some car fans on the Apple leadership team, including the company’s marketing executives, were resistant to building a product that didn’t look and feel like a car. Services head Eddy Cue suggested that it might be more prudent to just try to make a better Tesla rather than invent an entirely new category of machine.
Similar disagreements played out within Project Titan itself. Steve Zadesky, a former Ford engineer and iPhone executive in charge of much of the car effort, imagined the company starting off with limited self-driving features that could then be improved. Others held fast to Level 5. Perica, the mergers-and-acquisitions chief who’d pushed to buy Tesla, told the Apple car team that the company should build “the first bird,” not “the last dinosaur.” When the group first began staffing up in 2015, the goal was to bring something to market by 2020.
Under Ive, the microbus design emerged. The interior would be covered in stainless steel, wood and white fabric. Ive wanted to sell the car only in white and in a single configuration so it would be instantly recognizable, like the original iPod he’d designed. At one point, the group briefly discussed a more traditional SUV-like design, as well. The team’s secret facility in Sunnyvale, California, was packed with car cabin prototypes and simulators. “It looked like you entered Disneyland—it was chock-full of toys,” says someone who worked in the building.
The team played with several different ideas for the interior, including installing a pair of specialized touchscreens suspended with brackets from the ceiling to control the car from both sides of the cabin. It also engineered microphones to be placed outside the vehicle to bring external sounds into the cabin, something passengers in non-Apple cars did by rolling down a window. “They would add all sorts of crazy features to the car and then realize those were bad ideas and pull them back out, leading to another cockpit redesign,” says an Apple executive with knowledge of the frequent changes.
Throughout much of the process, Apple continued exploring partnerships. Riccio and Zadesky, years after Cook shot down buying Tesla, met with Musk to discuss ways they could collaborate, including the possibility of Tesla producing batteries for the Apple car. That prospect didn’t advance. Musk, who didn’t respond to a request for comment for this story, at one point publicly called Apple a “Tesla graveyard” full of engineers he’d fired. A few years later, he tried to restart talks with Cook as Tesla struggled to build the Model 3. Musk has said the Apple CEO wouldn’t meet.
Talks with Mercedes-Benz progressed further. For a few months, Apple and the German automaker actively worked on a partnership similar to the Tesla idea, but with a twist. Mercedes would manufacture Apple’s vehicle, while it would also sell its own cars with Apple’s self-driving platform and user interface. Apple eventually pulled out, in part because the early work gave its executives confidence they could build a car on their own, people involved in the failed deal say.
At other points, Apple held exploratory acquisition talks with car companies beyond Tesla. The closest it got to a deal was with McLaren. Some Apple executives believed that scooping up the British automaker, which makes a few thousand cars by hand each year and sells them to the super rich, would excite Jony Ive, who’d scaled back his involvement at Apple after the launch of the Apple Watch, and reengage him with the company. The proposed deal, before it fell apart, would have provided Ive with a new design studio in London. Other discussions with BMW AG and, much later, Canoo Inc.—an electric-vehicle startup with a decidedly Apple-esque design aesthetic—went nowhere.